
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VECTOR AND RASTER DATA IN GIS CODE
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VECTOR AND RASTER DATA IN GIS SERIES
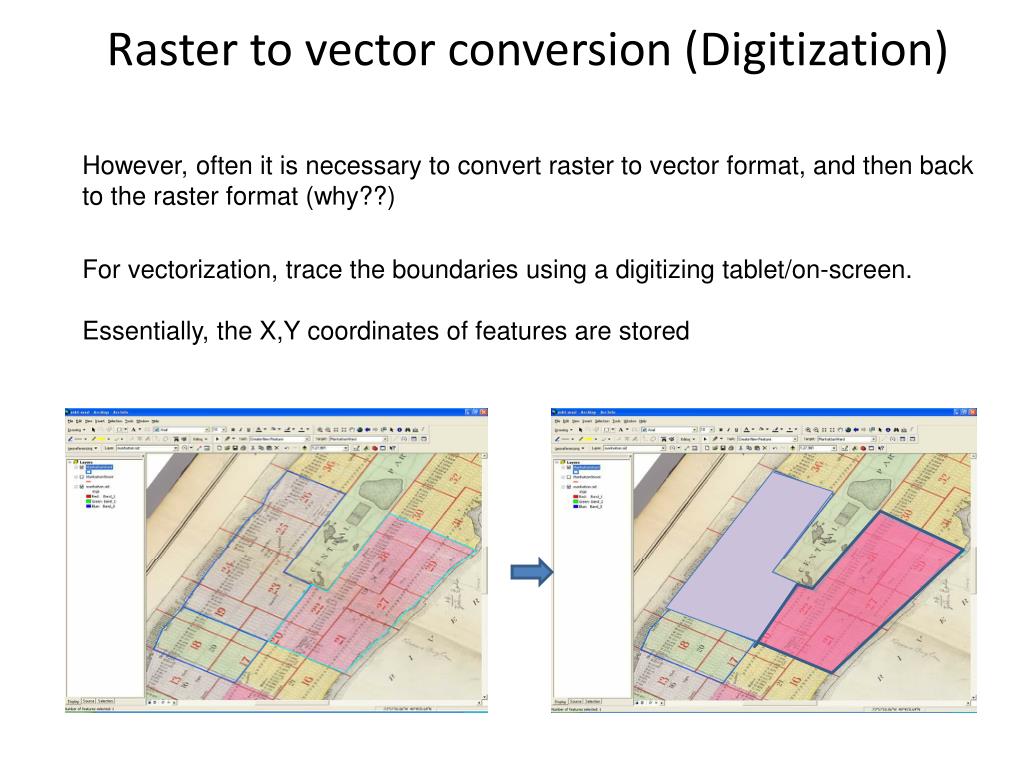
They provide an effective method of storing the continuity as a surface. Rasters are well suited for representing data that changes continuously across a landscape (surface). Below is an orthoimage as a basemap for road data. Three main sources of image basemaps are orthoimages from aircraft, satellite imagery, and scanned maps. For example, orthoimages displayed underneath other GIS layers provide the map user with confidence that map layers are spatially aligned and represent real objects, as well as additional information. Within a GIS, the uses of raster data fall under four main categories:Ī common use of image data in a GIS is as a background display for other feature layers. While the structure of raster data is simple, it is exceptionally useful for a wide range of applications. Picture rasters are often used as attributes in tables-they can be displayed with your geographic data and are used to convey additional information about map features. Pictures include scanned maps or drawings and building photographs.Ĭontinuous and thematic rasters may be displayed as data layers along with other geographic data on your map but are often used as the source data for spatial analysis with the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst or ArcGIS Image Analyst extension.Thematic data (also known as discrete) represents features such as land use or soils data.Continuous data represents phenomena such as elevation and spectral image data collected from satellites and airborne platforms such as drones.Rasters are digital aerial photographs, imagery from satellites, digital pictures, or even scanned maps.ĭata stored in a raster format represents real-world phenomena: Raster vs vectorīoth types of data are very useful, but there are important differences.In its simplest form, a raster consists of a matrix of cells (or pixels) organized into rows and columns (or a grid) where each cell contains a value representing information, such as temperature. The vector version can also store additional context information about these features – the attributes – a very important aspect. To reproduce the building in a GIS the computer reads these values and draws a line linking the coordinate positions.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VECTOR AND RASTER DATA IN GIS SERIES
The position and shape of a building is captured as a series of four pairs of numerical coordinates.

A value is stored in each of these cells to represent the nature of whatever is present at the corresponding location on the ground. The entire area of the map is subdivided into a grid of tiny cells, or pixels. Raster data can be thought of as being similar to a digital photograph. These numerical values can be used to translate map information into digital form, in both vector and raster formats.

All locations and shapes can be defined in terms of x and y coordinates from a given grid system. These numbers refer to coordinates from the British National Grid. Look at Ordnance Survey (OS) paper maps and you will notice, along the sides, there are a series of numbers associated with a grid covering the whole map area. These coordinate systems can be local, national or international. Coincidentally maps reference geographical locations on the earth's surface through a system of coordinates.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN VECTOR AND RASTER DATA IN GIS CODE
Computers store information in sequences of binary digits (bits), which form a code for every possible number or letter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
